You’ve spent hours crafting the perfect blog post, but it’s barely getting any traffic. Sound familiar? Many businesses struggle to rank on Google, not because their content isn’t valuable, but because it’s not optimised for search engines.
Google uses over 200 factors in its ranking algorithm? With so many moving parts, SEO can feel overwhelming.
The good news? You don’t need to be an SEO expert to get it right.
This 9-step checklist breaks everything down into actionable steps. You can optimise your content effectively, boost rankings, and drive more organic traffic – without the guesswork.
Let’s get started.
Key takeaways:
- Keyword research: Target the right search terms with a focus on intent and long-tail variations.
- Blog structure: Use clear headings, bullet points, and a table of contents for better readability.
- URLs, title tags, and meta descriptions: Keep them concise, keyword-rich, and compelling.
- Optimised content body: Place keywords naturally, avoid thin content, and aim for 1,500+ words.
- Internal and external links: Strengthen your blog with relevant links to improve SEO value.
- Image optimisation: Use descriptive filenames, alt text, and compressed images for faster loading.
- Technical SEO: Ensure your blog is mobile-friendly, fast, and correctly indexed.
- Engagement and social sharing: Encourage readers to comment, share, and interact with your content.
- Updating and repurposing: Regularly refresh content, update links, and repurpose for social media, infographics, and videos.
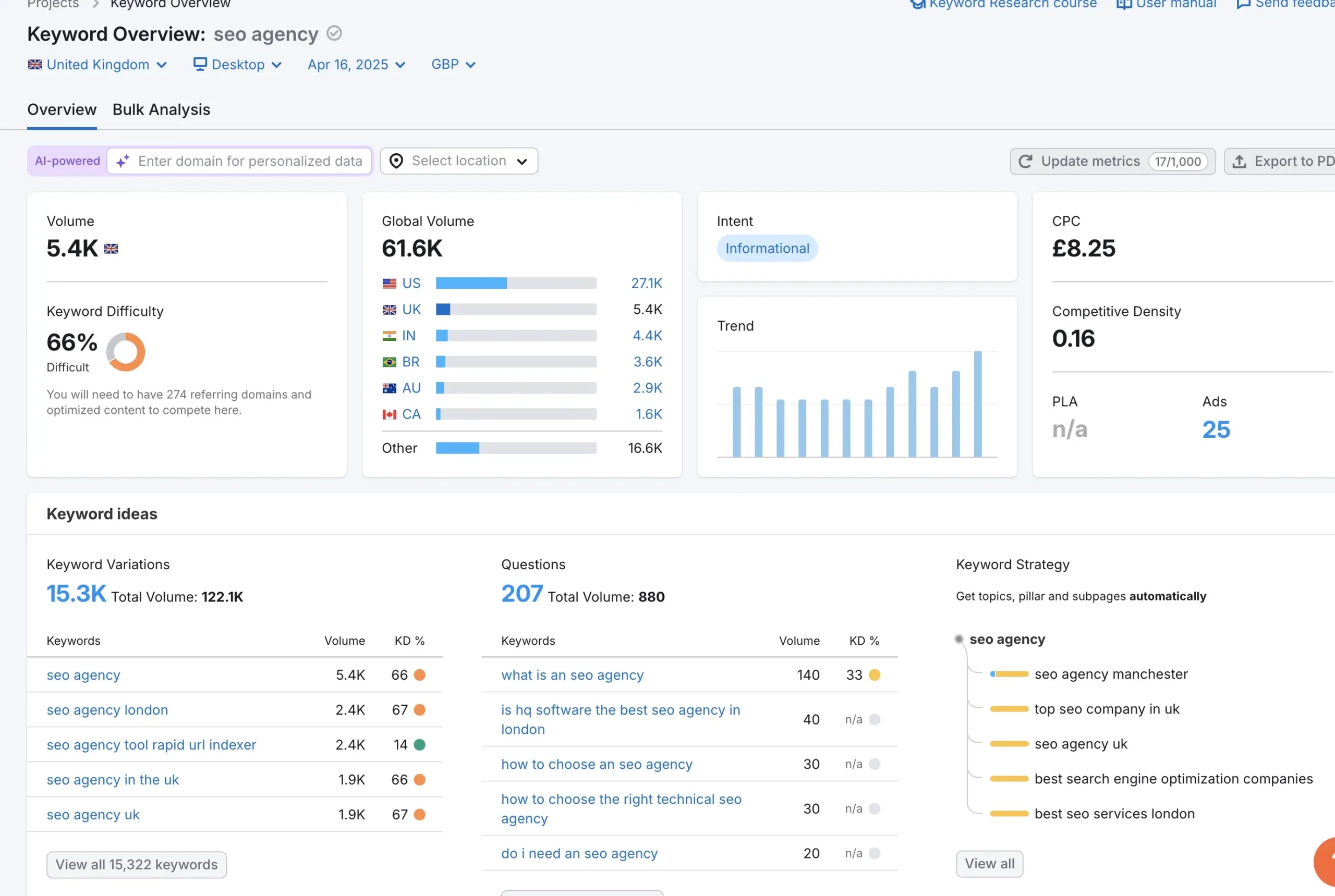
1. Keyword research
Find the right keywords
Choosing the right keywords is the first step in optimising your blog for SEO. Without targeted keywords, your content won’t reach the right audience.
To get started, use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, and Ahrefs to find relevant search terms. Focus on keywords that align with your business goals and the search intent of your audience.
Search intent falls into four main categories:
- Informational: The user is looking for general knowledge or advice.
Example: “What is SEO?” or “What does SEO stand for?”
- Navigational: The user is searching for a specific website or page.
Example: “SEO checker” or “Yoast SEO”
- Commercial: The user is interested in a brand, product or service.
Example: “Local SEO” or “SEO agency”
- Transactional: The user is ready to take action (buy, sign up, enquire).
Example: “SEO marketing services” or “SEO packages”
For lead generation, focus on commercial and transactional keywords – these are the searches made by people ready to convert.
Long-Tail Keywords & Semantic Variations
Not all high-traffic keywords are easy to rank for. If your main keyword is too competitive, long-tail keywords (4+ words) can be a great alternative.
For example, instead of targeting “SEO”, try:
- “SEO company for small business”
- “SEO for plumbing contractors”
Use the following tools to find long-tail variations:
- Google Autocomplete (see what suggestions appear when you start typing)
- People Also Ask (PAA) (questions that show up in Google search results)
- Answer The Public / Also Asked (find related questions and topics)
Incorporating semantic variations – keywords related in meaning – can also improve your rankings. For example, if targeting “SEO checklist”, you might include:
- “ How do you optimise a blog for SEO?”
- “On-page SEO for blog posts”
- “How to rank blog content in Google”
By focusing on the right keywords, you increase your chances of attracting qualified traffic that is ready to engage with your content
Related: An introduction to basic SEO
2. Structuring your blog for maximum readability and SEO value
A well-structured blog post is easier to read, keeps users engaged, and improves SEO. Google prioritises content that is clear, organised, and easy to navigate. A strong structure also increases the chances of earning featured snippets and ranking for People Also Ask (PAA) questions.
H1: One clear, keyword-optimised title
Your H1 (main heading) should be clear, relevant, and include the primary keyword naturally. It should accurately describe what the blog is about without sounding forced.
Good examples:
- Blog SEO checklist: A 9-step guide to boost rankings in 2025
- SEO checklist for blog posts: How to optimise your content for Google
Avoid:
- Blog SEO checklist SEO blog best guide (keyword stuffing)
- Best SEO tricks and hacks (too vague)
Related: How to create irresistible blog titles for your audience
H2s and H3s: Use keyword variations and answer common questions
Headings help break up content, making it skimmable for readers and easier for search engines to understand.
- H2s should cover key topics using primary or semantically related keywords.
- H3s should support the H2 by expanding on subtopics or answering specific questions.
Use People Also Ask (PAA) questions from Google to guide your subheadings. These are the queries users frequently search for. If competitors haven’t answered them properly, this is an opportunity to provide better, more in-depth content.
Example heading structure:
- H2: How do you optimise a blog for SEO?
- H3: What are the key elements of a blog SEO checklist?
- H3: How do keywords impact blog rankings?
Bullet points and lists: Help capture featured snippets
Bullet points and numbered lists make content easier to scan and improve readability. Google often pulls information from lists for featured snippets, which can increase visibility in search results.
Use bullet points for:
- Step-by-step processes (e.g. how to optimise a blog)
- Quick tips or best practices
- Summarising key takeaways
Use numbered lists for:
- Ranked or ordered content (e.g. a step-by-step SEO guide)
- Comparisons and recommendations
To target your copy for a featured snippet:
- Use short, clear answers directly below an H2 or H3.
- Lists or tables increase the likelihood of Google pulling your content.
- Include keywords in the list introduction (e.g., “Here’s a step-by-step blog SEO checklist to help your content rank higher:”).

Short paragraphs: Improve readability
Keeping paragraphs short and concise improves readability and keeps readers engaged. Aim for 2-3 sentences per paragraph.
Google prefers content that is easy to read, and so do users. Use tools like the Hemingway Editor to check sentence length and readability.
Table of contents: Improve user experience and SEO
Adding a table of contents at the beginning of longer blogs helps:
- Improve user experience (UX) by making navigation easier.
- Encourage readers to explore specific sections without scrolling.
- Help Google understand content structure, improving the chances of ranking for different queries.
A clickable table of contents also increases time on page – a key ranking factor – by helping users quickly find the information they need.
By structuring your blog correctly, you create a better reading experience while improving your chances of ranking higher in search results.
3. URL, title tags, and meta descriptions
Optimising your URL, title tag, and meta description helps improve click-through rates (CTR) and makes your blog post more appealing in search results. These elements are often the first thing users see, so they need to be clear, engaging, and keyword-rich.

URL best practices
A clean, descriptive URL improves readability and search rankings. Google prefers short, structured URLs that give users a clear idea of what the page is about.
Best practices:
- Keep URLs short and simple (avoid unnecessary words).
- Include the primary keyword naturally.
- Use hyphens (-) instead of underscores (_) or spaces.
- Avoid stop words like and, the, to, of.
Example:
✅ /blog-seo-checklist/ (good: short, keyword included)
❌ /how-to-optimise-a-blog-for-seo/ (too long, includes stop words)
A well-structured URL helps both users and search engines understand the topic of your blog.
Title tag best practices
Your title tag is one of the most important on-page SEO factors. It tells Google (and users) what your blog is about. A strong title can increase clicks and improve rankings.
Best practices:
- Include the main keyword near the start.
- Keep it under 60 characters to avoid truncation in search results.
- Make it compelling and benefit-driven—encourage users to click.
- Use title case.
Example:
✅ Blog SEO checklist: A 9-step guide to boost rankings in 2025
❌ How to improve your blog’s SEO with an amazing checklist for better rankings (too long, unclear, lacks focus)
Meta description tips
A meta description gives a short summary of your blog post in search results. While not a direct ranking factor, a well-written meta description increases CTR, bringing more visitors to your site.
4. Optimising blog content body
Optimising the body of your blog post is essential for both SEO and user experience. A well-structured, informative, and engaging post helps search engines understand your content while keeping readers on the page.
Include target keywords naturally
Using your primary keyword is important, but it must fit naturally within the text. Google penalises keyword stuffing, so focus on flow and readability.
A good approach is to use synonyms and semantically related keywords instead of repeating the exact phrase. This helps search engines understand the topic without making the content sound forced.
Example:
✅ “A well-optimised blog follows key SEO principles, such as keyword placement and content structure.”
❌ “This blog SEO checklist will help you with blog SEO. Blog SEO is important for blog SEO rankings.” (repetitive and unnatural)
Use LSI and semantic keywords to improve relevance
Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords and semantic variations give context to your content. These are related terms that search engines expect to see when discussing a topic.
For a blog post about SEO checklists, useful semantic keywords might include:
- On-page SEO
- Blog optimisation
- Search rankings
- Organic traffic
- Keyword placement
Place the primary keyword in key locations
To maximise SEO value, place your primary keyword strategically throughout your blog:
- First 100 words – Introduce the topic with the keyword naturally.
- H1 title – The blog post title should include the keyword.
- At least one H2 subheading – Reinforces relevance.
- Image alt text – Helps Google understand images.
- Meta description – Encourages clicks from search results.
This ensures Google recognises your blog as highly relevant to the target search query.
Avoid thin content
Google favours in-depth, valuable content over short, superficial articles. Aim for a minimum of 1,500 words, but base the length on top-ranking competitor pages.
- Analyse competitors: Use tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs to see how long the top-ranking blogs are.
- Go deeper: If competitors cover 8 tips, provide 9 or 10, adding unique insights or real-world examples.
- Make it scannable: Use headings, bullet points, lists, and visuals to break up text.
A well-optimised blog post is not just keyword-rich, but structured, valuable, and easy to read—ensuring both search engines and readers find it useful.
5. Internal & external links
Effective linking improves SEO, helps users navigate your content, and strengthens your website’s authority. A well-structured internal linking strategy keeps visitors engaged, while external links signal credibility to search engines.
Internal links: Strengthen site structure and engagement
Internal links help search engines understand the relationship between pages on your site. They also guide users to relevant content, increasing time on site and reducing bounce rates.
Best practices:
- Add up to five internal links per blog post.
- Link to relevant blog posts or service pages (not just the homepage).
- Link to an important service page in the introduction.
- Link to related blogs within body paragraphs naturally.
- Link to a contact or services page with a CTA in the conclusion
- Use descriptive, keyword-rich anchor text (avoid “click here”).
Example:
✅ “For a deeper dive, read our SEO strategy guide.”
❌ “Click here for more SEO tips.”
Well-placed internal links support topic clusters, helping Google understand your expertise in a given area.
TIP: Remember to find internal links to link TO your new blog as well as. Find relevant blogs and pages with your target keywords and add links to your new blog.
| Ideal | Exact match | Includes the exact keyword you want to rank for |
| Ideal | Partial match | Contains a variation of the keyword you want to rank for |
| Ok | Branded | Contains your company name or terms unique to your domain |
| Avoid | Naked URLs | Includes plain URL, such as www.yourwebsite.com |
| Avoid | Generic | Provides the least amount of context, such as “click here,” “page,” or “read more.” |
External links: Boost credibility and trust
External links to high-authority sources add credibility to your content and improve user experience. Citing well-respected sites helps validate your information.
Best practices:
- Use 2-3 external links to trusted sources.
- Ensure links are recent (published within the last 12 months).
- Choose sources that support your claims or provide additional value.
Using links strategically
- Place the most important internal link early in the blog (preferably in the introduction).
- Add a relevant internal link in the conclusion to guide readers to another page.
- External links should open in a new tab to keep users on your site.
By linking strategically, you enhance both SEO performance and user experience, making your content more valuable and authoritative.
6. Image optimisation
Optimising images is essential for SEO, user experience, and page speed. Large or poorly labelled images can slow down your site and make content less accessible. A well-optimised image helps search engines understand your content and improves rankings.
Use descriptive filenames
Before uploading an image, rename the file to something clear and relevant. Google reads filenames to understand what an image is about, so avoid generic names like image123.jpg.
Best practices:
- Use keywords naturally but keep filenames concise.
- Separate words with hyphens (-), not underscores (_).
Examples:
✅ seo-blog-checklist.png (descriptive and keyword-rich)
❌ IMG2025.jpg (generic, no SEO value)
Optimise alt text
Alt text (alternative text) describes an image for search engines and visually impaired users. This improves SEO and accessibility.
Best practices:
- Clearly describe the image in natural language.
- Include a primary or related keyword where relevant.
- Avoid keyword stuffing – focus on readability.
Examples:
✅ “SEO checklist infographic outlining steps to optimise a blog post.”
❌ “SEO checklist blog SEO checklist blog post checklist SEO.” (unnatural and spammy)
Resize and compress images for faster loading
Large image files slow down your website, affecting SEO rankings and user experience. Compress images to under 100KB without losing quality using tools like:
- Photoshop (supports multiple formats, including JPEG and WebP)
- TinyPNG (free but less control)
Consider using WebP format, which offers better compression than JPEG or PNG.
By optimising your images, you improve page speed, enhance accessibility, and boost SEO rankings, making your blog more user-friendly and search engine-friendly.
| Image format | Best use case |
| JPEG | Best for large, high-quality photos. Compressed for speed. |
| PNG | Ideal for graphics with transparency but larger file sizes. |
| WebP | Best for modern web optimisation—faster and high quality. |
7. Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures that search engines can crawl, understand, and index your blog correctly. Even with great content, your blog won’t rank well if it has technical issues.
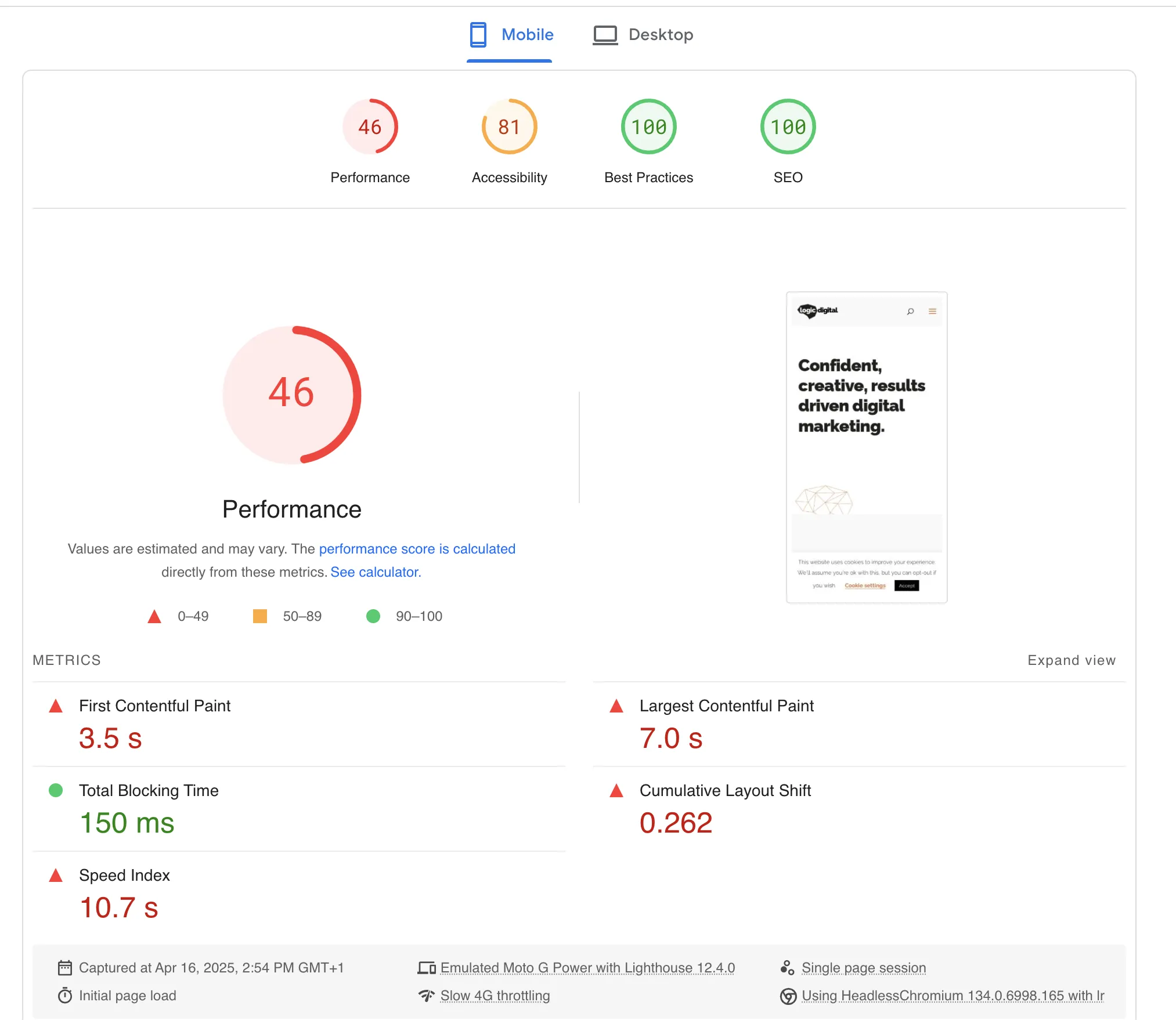
Mobile-friendly and fast loading
Google prioritises mobile-first indexing, meaning your blog must be fully optimised for mobile users. A slow-loading site also leads to higher bounce rates, reducing rankings.
Best practices:
- Test your page speed using Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Compress images and enable browser caching.
- Use a lightweight theme and minimise unnecessary scripts.
- Ensure text is readable on smaller screens and buttons are easy to tap.
- A well-optimised blog should load in under three seconds for the best user experience.
Use schema markup
Schema markup helps search engines understand the structure of your content. Adding blog schema can improve search visibility, increasing the chances of appearing in rich snippets.
Best practices:
- Use BlogPosting schema to help Google categorise your blog.
- Mark up elements like title, author, publish date, and main content.
- Use tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to check for errors.
Set canonical URLs
If your content is accessible under multiple URLs (e.g. with and without “www” or “https”), duplicate content issues can arise. A canonical tag tells search engines which version to index.
Best practices:
- Add a canonical tag in the blog’s HTML to specify the preferred URL.
- Use absolute URLs (full website address) rather than relative ones.
- Check that canonical tags are correctly set in Yoast SEO or Rank Math (if using WordPress).
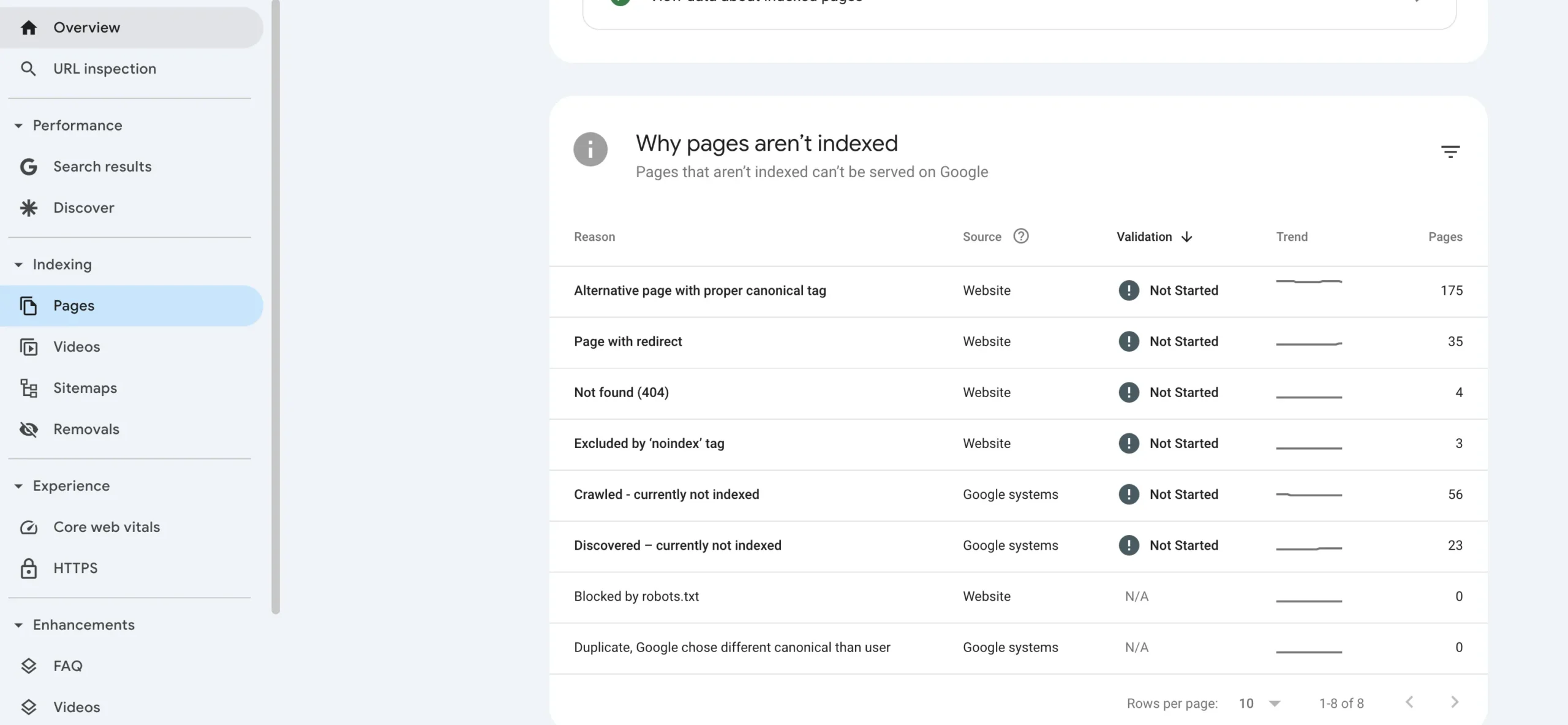
Check indexability
If your blog isn’t indexed, it won’t appear in search results. Some pages may be accidentally blocked from indexing due to a “noindex” meta tag or robots.txt rule.
Best practices:
- Use Google Search Console to check if your blog is indexed.
- Look for any “noindex” tags in your page’s HTML.
- Ensure robots.txt doesn’t block important pages from being crawled.
By implementing technical SEO best practices, you ensure your blog is fast, mobile-friendly, and easily discoverable, giving it the best chance of ranking in Google search results.
8. Encouraging engagement & social sharing
Driving engagement isn’t just about getting visitors to your blog – it’s about keeping them engaged and encouraging them to share your content. The more users interact with your blog, the more search engines see it as valuable and relevant, which can improve rankings.
Make sharing easy with social plugins
If readers find your content useful, they’re more likely to share it – but only if it’s easy to do.
Best practices:
- Add social sharing buttons using plugins like AddThis, ShareThis, or Sumo.
- Place sharing buttons at the top and bottom of your blog.
- Make sure sharing works across LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, and email (depending on your audience).
Encourage readers to comment and engage
User engagement signals to Google that your content is valuable. Encouraging comments, discussions, and questions can increase time on page and return visits.
Best practices:
- End with a call-to-action (CTA) prompting readers to share their thoughts.
- Ask open-ended questions related to the blog topic.
- Respond to comments to keep the conversation going.
Example CTA:
” Have you tried this technique? What worked for you?”
By making it easy to share, interact, and engage, your blog can reach a wider audience while boosting SEO through increased dwell time and user interaction.
9. Updating & Repurposing Old Content
SEO isn’t just about creating new content – it’s also about keeping existing content fresh and relevant. Google rewards up-to-date, high-quality content, so regularly reviewing, updating, and repurposing your blog posts can help maintain and improve rankings.
Track performance in Google Search Console and GA4
Monitoring your blog’s performance helps identify content that needs improvement.
Best practices:
- Use Google Search Console (GSC) to check impressions, clicks, and rankings.
- Look for keywords ranking in positions 4-20 – these are opportunities to push content higher.
- Use Google Analytics 4 (GA4) to track engagement, bounce rates, and conversions.
If a blog post is losing traffic, it may need new information, better optimisation, or additional insights.
Update stats and links every 12 months
Outdated content loses credibility. Regularly refreshing stats, links, and references improves accuracy and trustworthiness.
Best practices:
- Replace old statistics with the latest data (use sources no older than 12 months).
- Check external links – ensure they still work and point to recent, authoritative sources.
- Expand or improve sections that are underperforming based on analytics.
Repurpose content for more visibility
A single blog post can be transformed into multiple content formats to reach a wider audience.
Repurposing ideas:
- Social media snippets – Share key takeaways as LinkedIn posts, Twitter threads, or Instagram carousels. Use blog sections for carousel posts on LinkedIn.
- Infographics – Convert a step-by-step checklist into a visually engaging infographic.
- YouTube videos – Turn blog content into explainer videos, tutorials, or webinars.
- Email marketing – create an email series from the blog content.
- Webinar – turn your blog into a webinar topic.
By refreshing and repurposing your blog content, you extend its lifespan, increase reach, and keep it relevant in search rankings.
Start optimising your blog today!
A well-optimised blog doesn’t just help with rankings – it attracts more readers, keeps them engaged, and drives conversions. By following this 9-step blog SEO checklist, you can create high-quality, search-friendly content that performs well in search results.
Need help optimising your website for SEO? Our expert team can help you create and refine content that ranks higher, drives traffic, and delivers results.
Contact our SEO experts today.
Boost rankings in 2025 – FAQs
How do I check my website ranking in Google?
You can search the keywords you want to rank for and see where your blog shows up, but this will only give you a very rough idea.
Tools like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or Semrush will give you a clearer picture of how your blog’s performing in search.
How do I improve my Google search ranking?
Focus on writing helpful content that matches what people are searching for. Use clear headings, include your main keywords naturally, add links to other pages, and make sure your site loads quickly, especially on mobile!
How do I write a blog for SEO?
To boost the SEO value of your blog posts:
– always have a clear title
– focus on one main topic
– include keywords in the right places (like your headings)
– use short paragraphs
– Include some links to other pages and (reputable) websites
Adding a good meta description, schema, and image alt text can also help you boost the power of your blog posts in Google’s search results!
How long should a blog be for SEO?
There’s no exact number, but you should always aim to have enough words to cover the topic properly, without waffling.
Around 1,000–1,500 words is a good starting point, as long as it’s useful and easy to read
Do I need to update my blog posts?
Yes, you definitely should!
If something’s out of date or no longer useful, give it a refresh.
Updated posts often perform better in search and show Google that your content is still relevant for searchers.



